|
utils-lists 4.0.0
µOS++ C++ intrusive lists utilities
|
|
utils-lists 4.0.0
µOS++ C++ intrusive lists utilities
|
The C++ standard libraries offer comprehensive support for various lists; however, most of them demand dynamic memory allocations for list nodes (the objects to store the pairs of links), which, on embedded systems, may be challenging; thus, when possible, it is preferred to avoid them, particularly at system level.
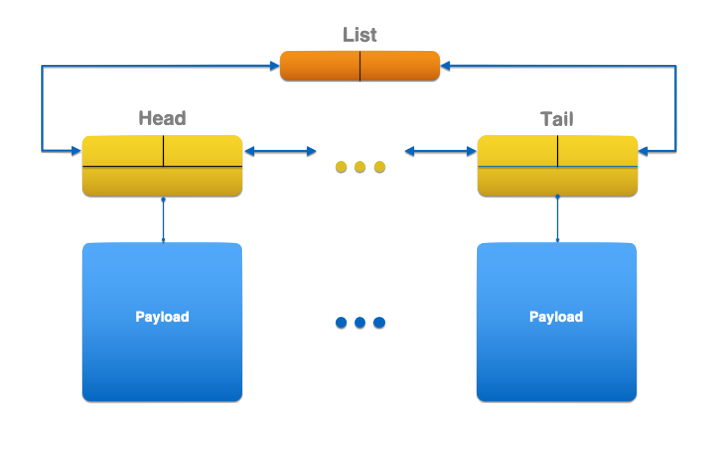
One possible way to avoid the dynamically allocated list nodes is to embed the list links into the payload objects. This is the method used by the intrusive lists. They are double linked lists that keep two pointers inside each linked object. Objects that belong to multiple lists have multiple pairs of pointers, one for each list.
At the implementation level, this can be achieved by using composition, with the objects storing the pairs of links being members of the payload objects.

For lists that are known to be linked into a single list, there is a simpler variant, with the payload object being derived from the object storing the pairs of links.

In order to support objects that auto-register themselves to static registrar objects, which are lists created via the static constructors mechanism in the global scope, it is mandatory to guarantee that the registrar is initialised before the clients need to register. Given that, as per the C++ standard, the order in which the static constructors are invoked is not determined, the only solution is to initialize the registrar before the static constructors.
These statically allocated lists must not change the content of any of their members in the constructors, since this may very well happen after clients have already registered.
Before inserting anything into these lists, the user must call initialize_once(), the will check the list, and, if still in the initial zero state, will initialise it to the empty state (with both pointers pointing to itself).
The definitions are grouped in a namespace below micro_os_plus:
The intrusive lists can be defined by instantiating a class template:
See the reference Intrusive double linked lists page.
For simpler use cases, like traditional list or low intrusive lists, there is a simpler template:
See the reference Double linked lists page.
The C++ methods available for the list are:
Forward iterators are defined as usual:
Individual nodes (derived from double_list_links_base) provide the following methods:
There are no C equivalents for the C++ definitions.
An example showing how to use the intrusive lists is available in tests/src/sample-test.cpp.
Here are some excerpts:
memset(), for example), before invoking the constructor via placement new.